


What are Dangerous Goods?
Main ContentIntroduction
What are Dangerous Goods ("DG")?
Most DG in Hong Kong are imported and exported by sea. With effect from 31 March 2022, the local DG classification system and packing, marking and labelling requirements have harmonised with the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (“IMDG Code”).
However, not all DG under the IMDG Code are classified as DG in Hong Kong, and not all DG included in the regulatory system are regulated by Fire Services Department (“FSD”).
We are the regulatory authority for all classes of DG on land, except gases under the Gas Safety Ordinance, Cap. 51[1], and Schedule 1 dangerous goods which is regulated by the Civil Engineering and Development Department. The Marine Department is the regulatory authority for DG at sea and cargo terminals.
[1] Gases under the Gas Safety Ordinance, Cap. 51 is controlled by the Electrical and Mechanical Services Department.
The DG regulated by FSD are stipulated in Parts 2 – 4 of Schedule 2 and Schedule 3 of the Dangerous Goods (Application and Exemption) Regulation 2012 (“Cap. 295E”). Tabulated below are the classes of DG under the regulation.
|
Class |
Properties |
Label[3] |
|
2.1 |
Flammable gases |
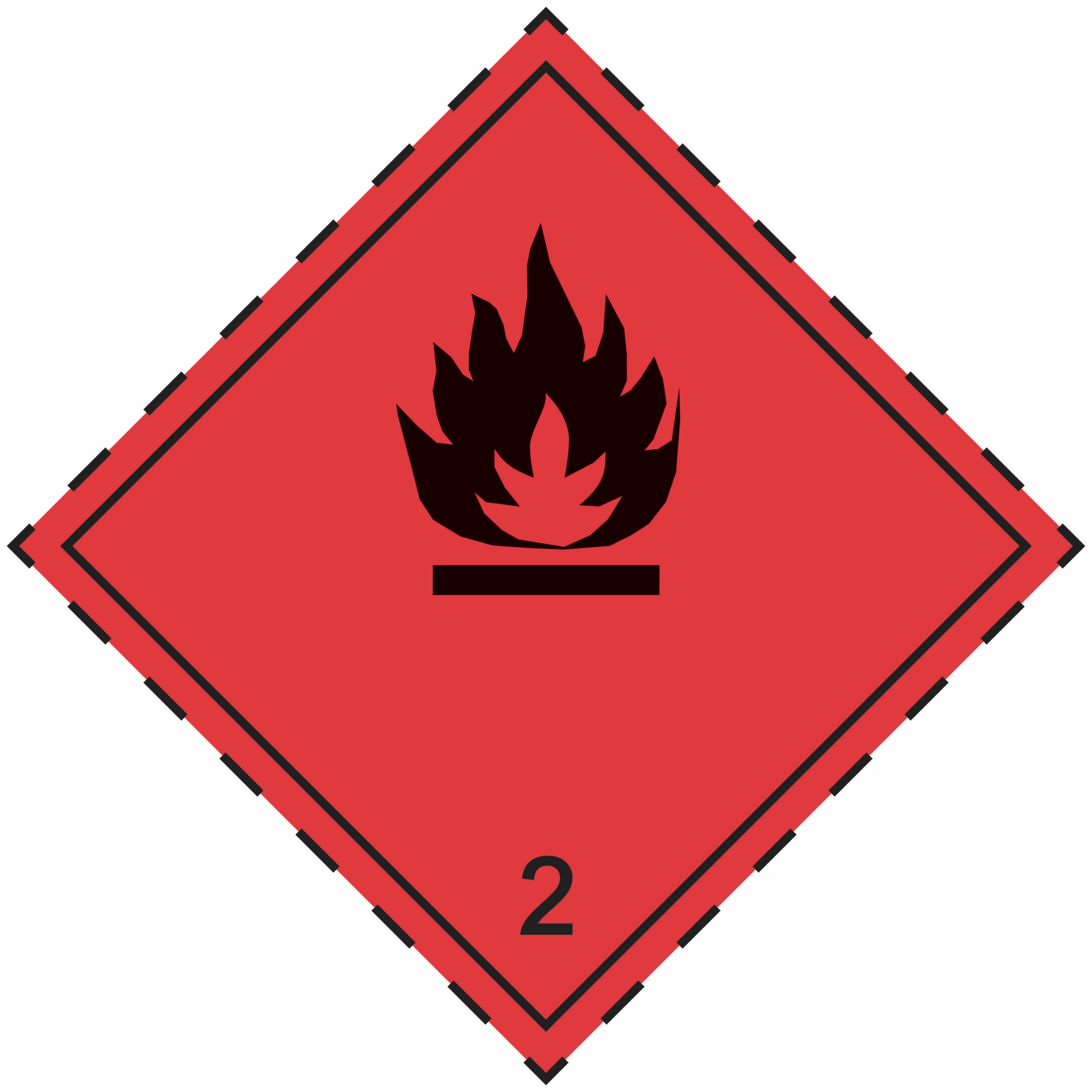 |
|
2.2 |
Non-flammable, non-toxic gases |
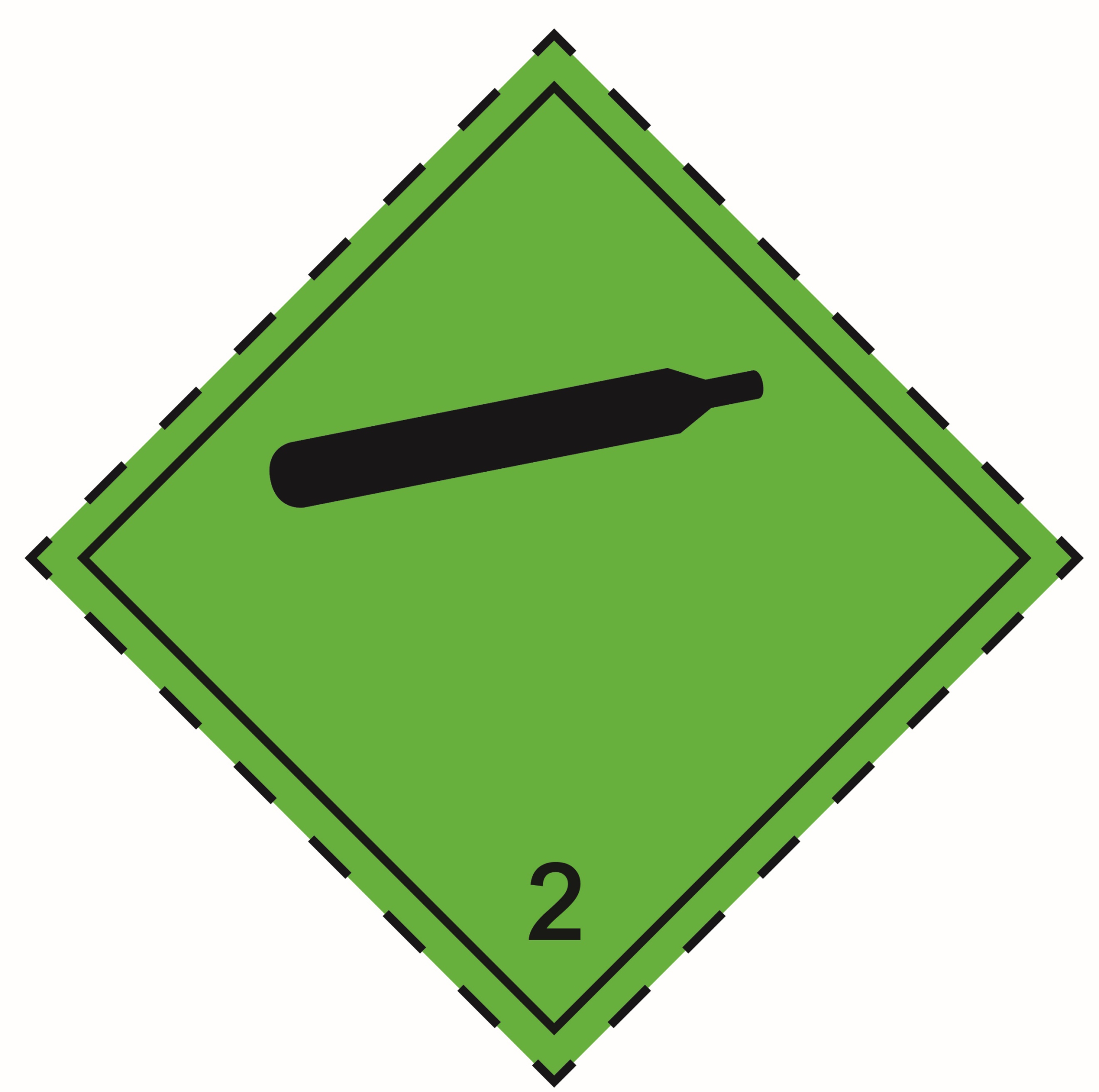 |
|
2.3 |
Toxic gases |
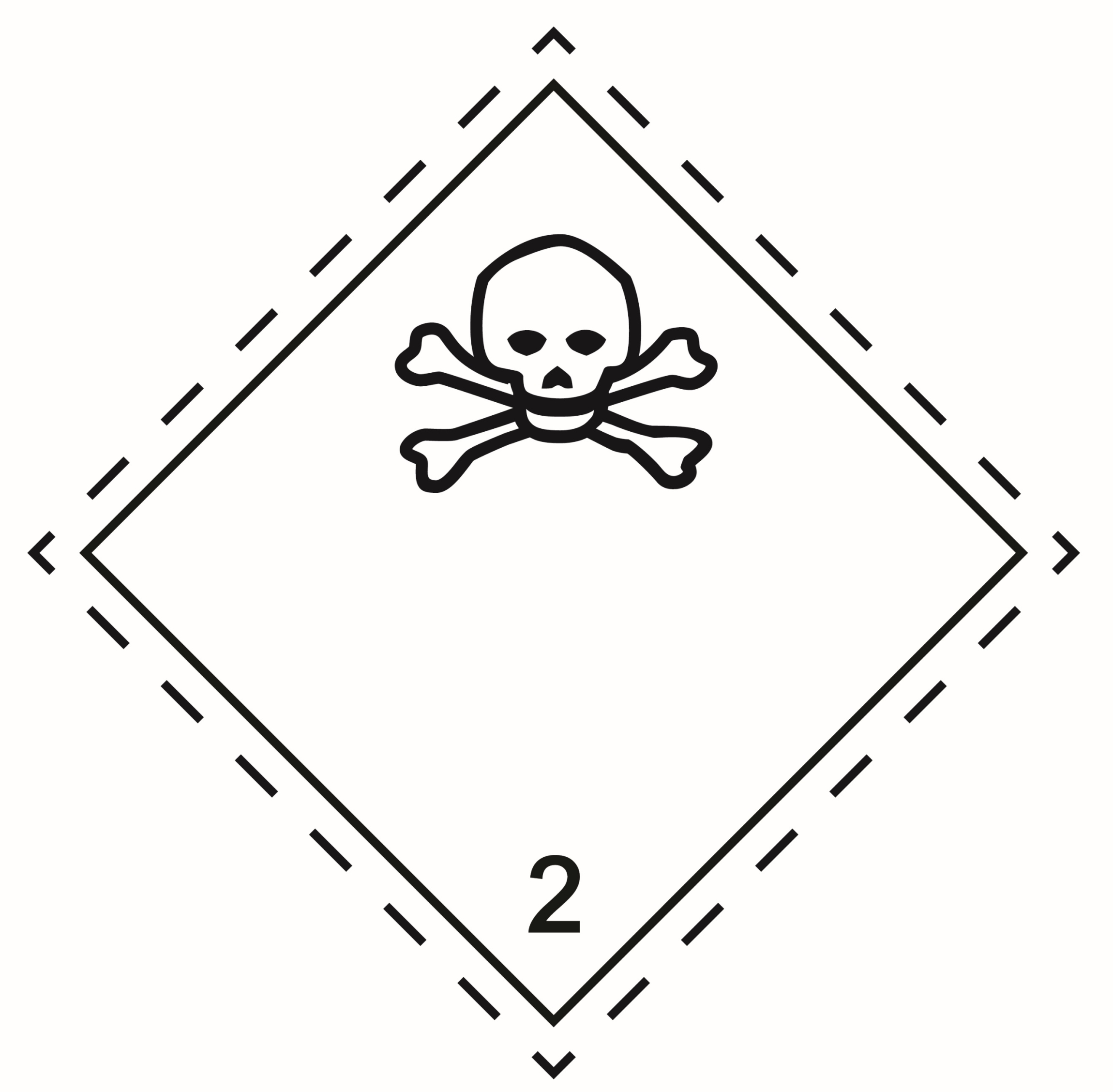 |
|
3 |
Flammable liquids having a flash point not exceeding 60oC (140 oF) in closed cup test
|
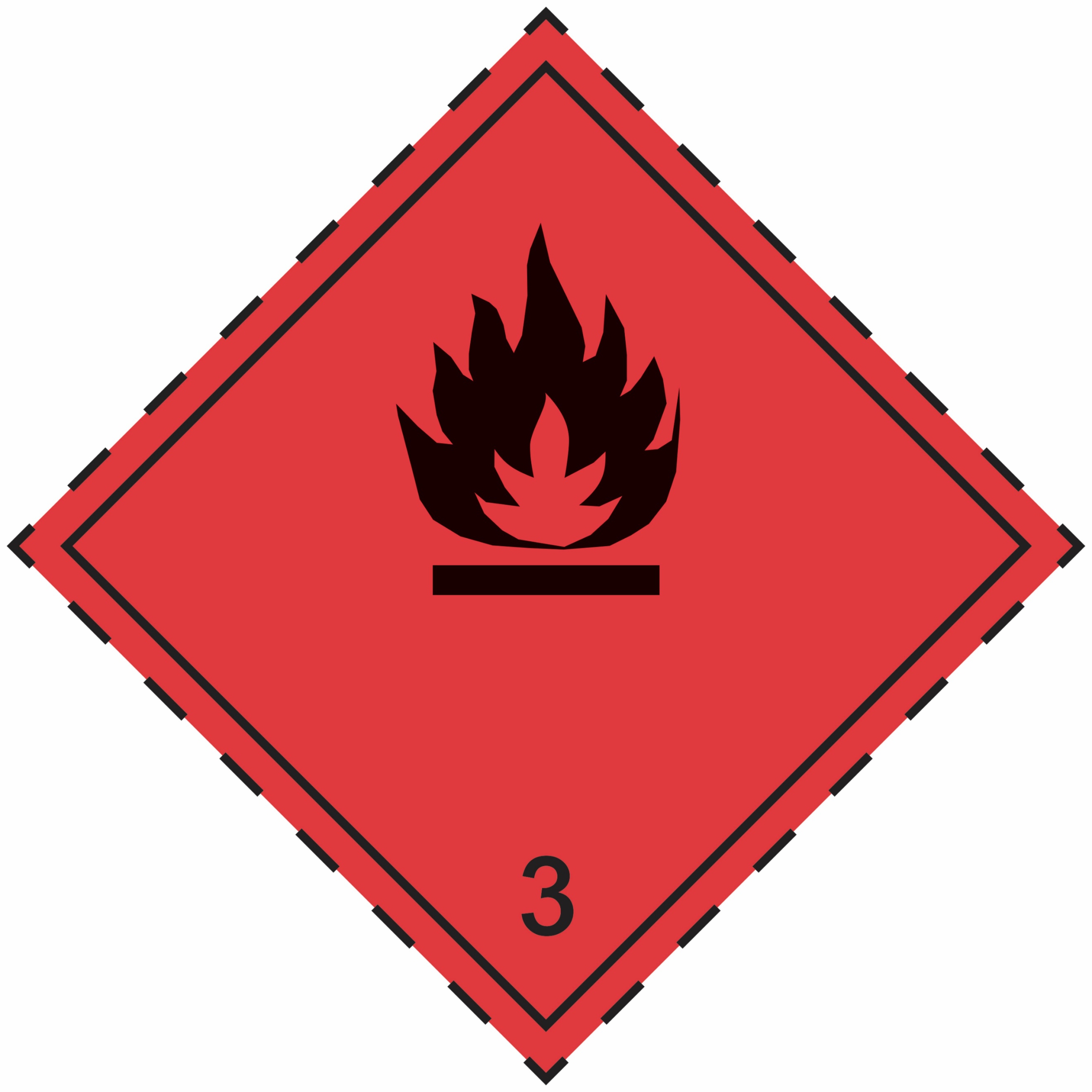 |
|
3A |
Diesel, fuel oil and furnace oil having a flash point exceeding 60oC (140 oF) in closed cup test |
 |
|
4.1 |
Flammable solids, self-reactive substances, solid desensitized explosives and polymerizing substances |
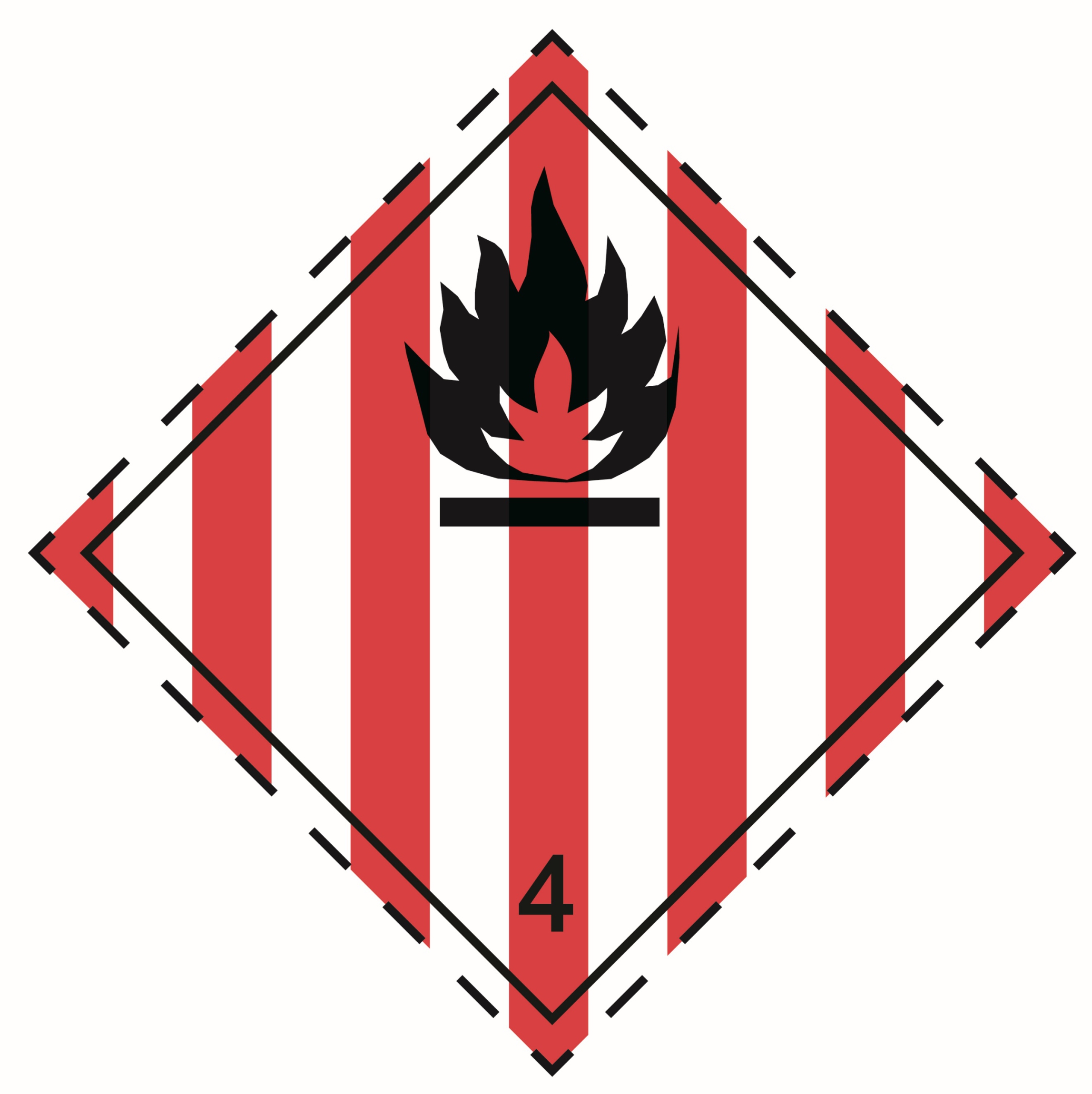 |
|
4.2 |
Substances liable to spontaneous combustion |
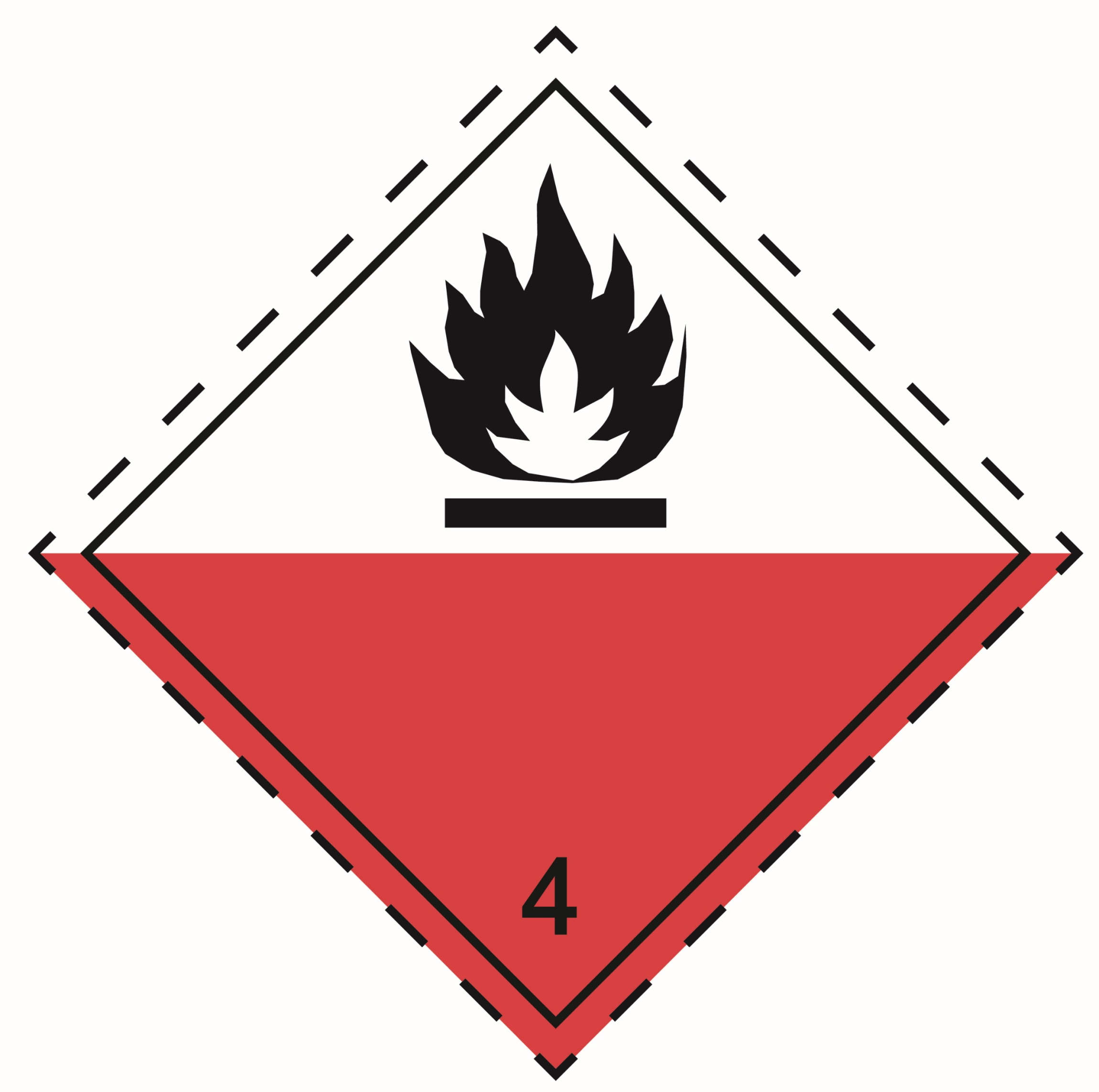 |
|
4.3 |
Substances which, in contact with water, emit flammable gases |
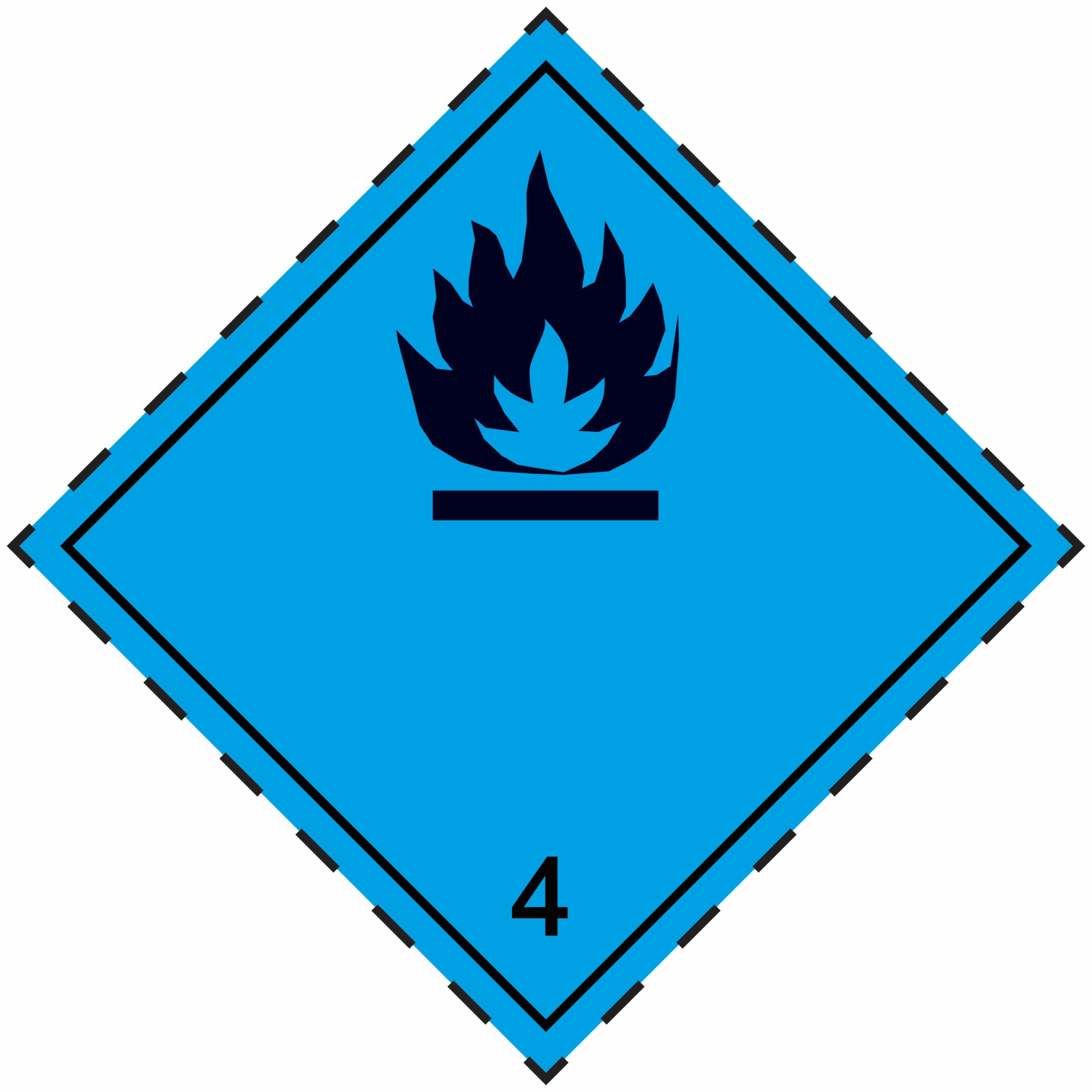 |
|
5.1 |
Oxidizing substances |
 |
|
5.2 |
Organic peroxides |
 |
|
6.1 |
Toxic substances |
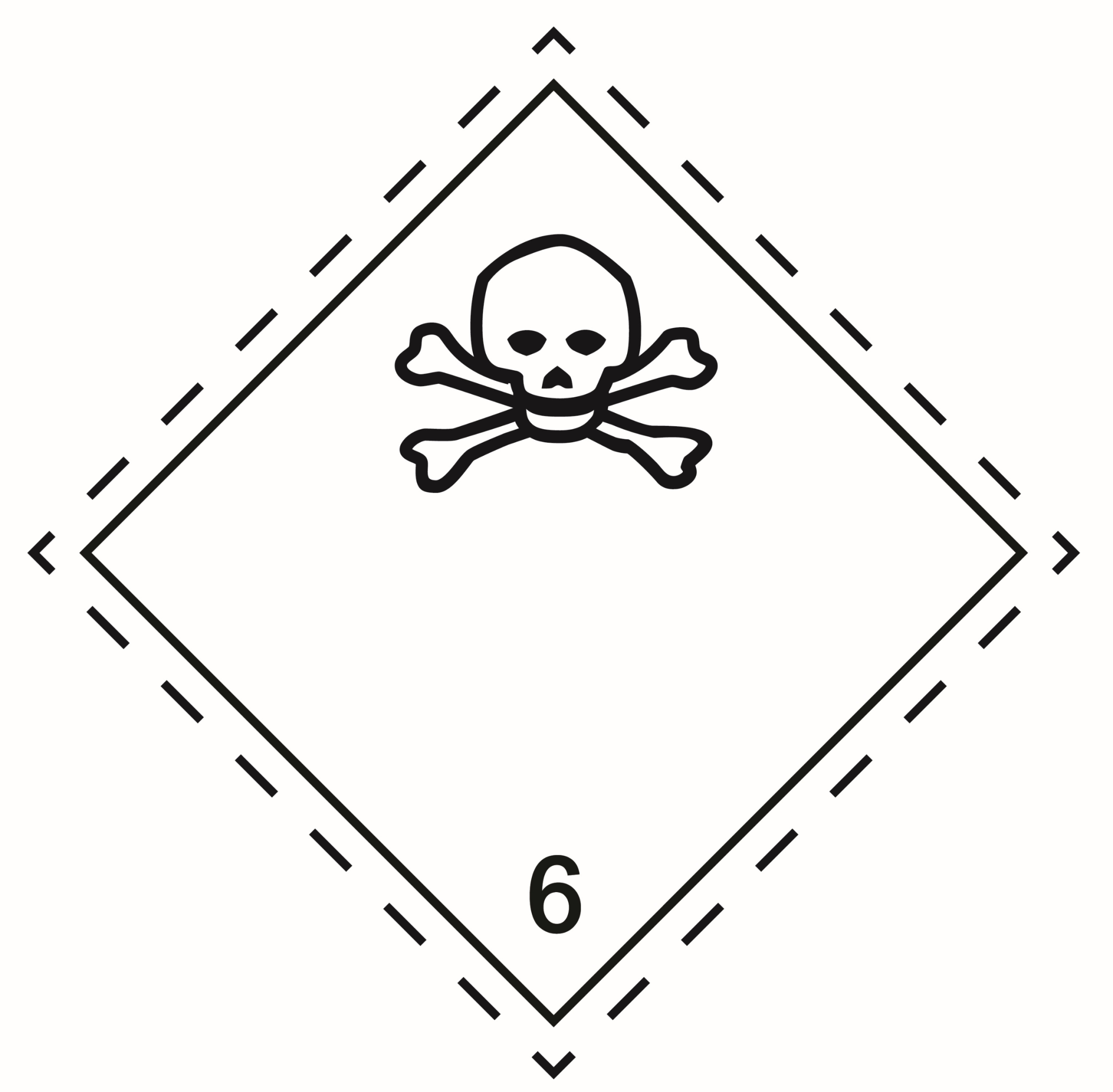 |
|
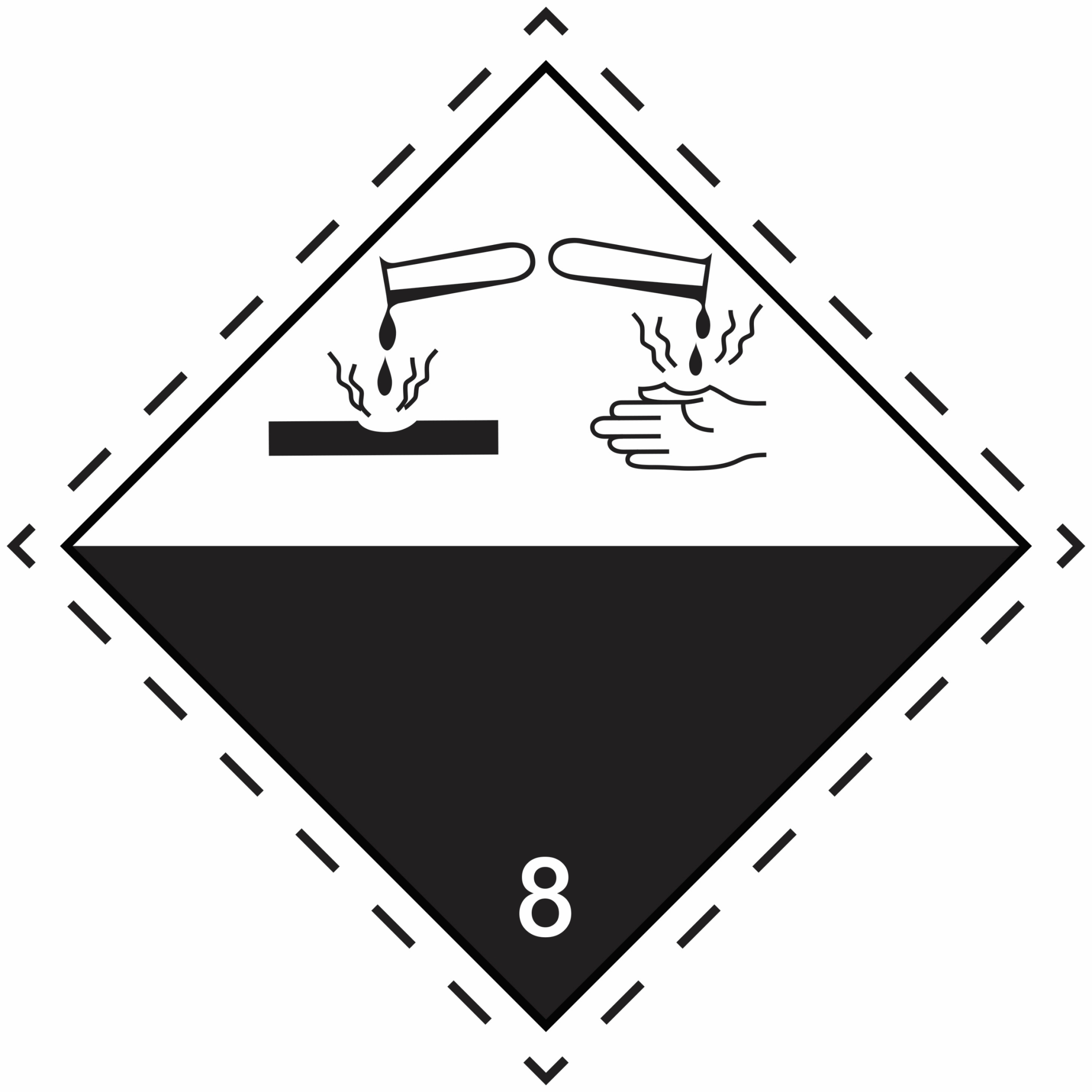
8 |
Corrosive substances |
 |
|
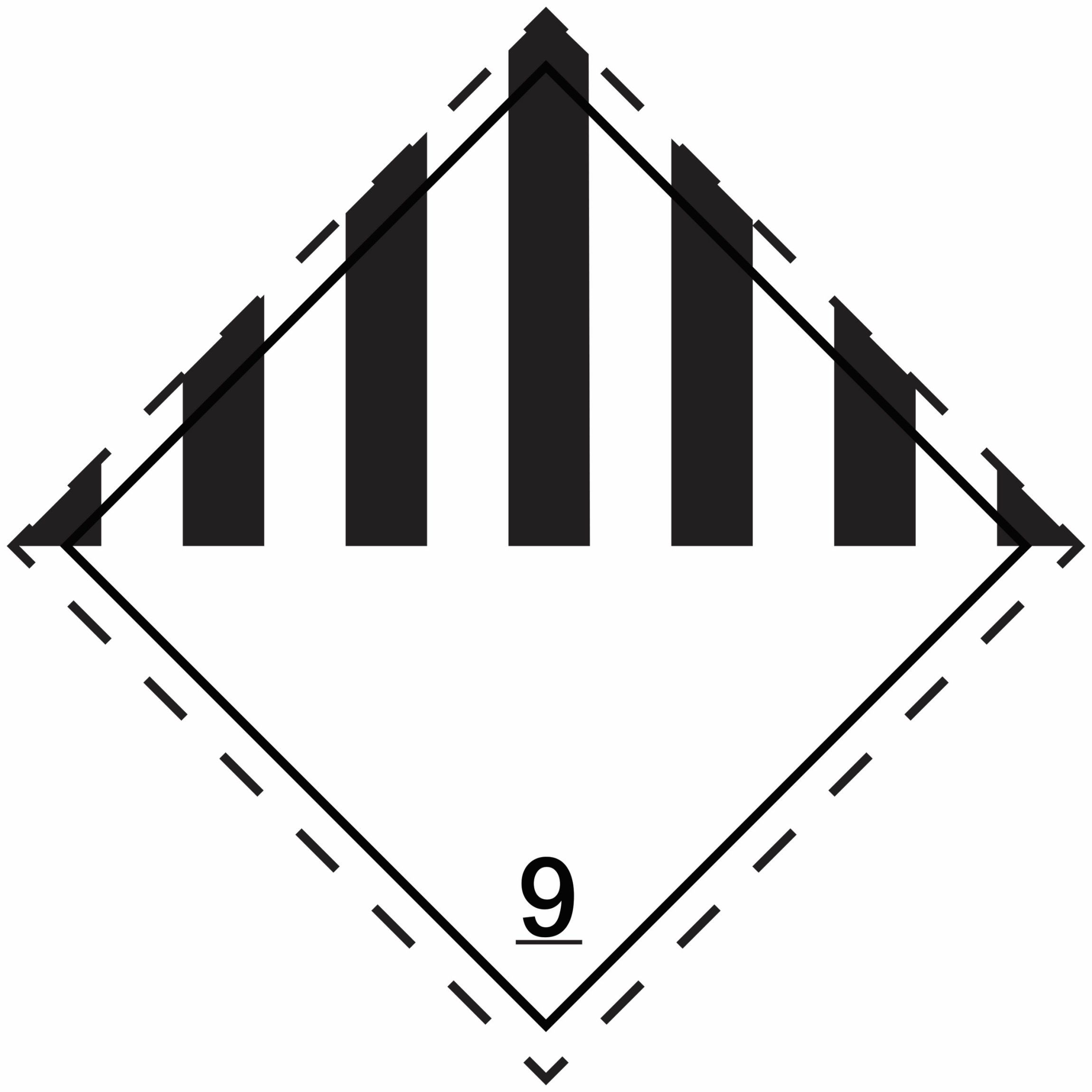
9 |
Miscellaneous dangerous substances and materials |
 |
|
9A |
Combustible goods which are exempt from the operation of sections 6, 8 and 10 of the DGO (s.30 of DG(A&E)R) 2012 |
Not applicable |
[3] There are more than one label for Classes 2 / 3 / 3A / 4 / 5 / 6.1 / 8 DG. Please refer to Schedule 6 – Part 3 – Division 2 of the Dangerous Goods (Control) Regulation for the form of labels for such DG.
How can you identify whether a DG is under FSD regulation?
For simplicity, if you wish to check whether a substance is regarded as a DG regulated by FSD, you may use the “Search Engine” of our website and enter either the “United Nations Number” or “Proper Shipping Name” as key word.
United Nations Number (UN No.)
UN No. contains the serial number assigned to the article or substance under the United Nations system. In relation to Schedule 2 dangerous goods (“S2DG”), UN No. means the number specified in column 1 of the table in Part 2 or 3 of Schedule 2 in relation to the DG and preceded by the alphabets “UN”.
For example, “CALCIUM CARBIDE” is assigned with “UN 1402”.
Proper Shipping Name (PSN)
Proper shipping name refers to the description of a DG in CAPITAL letters (plus any numbers, Greek letters, “sec”, “tert” and the letters m, n, o, p, which form an integral part of the name) as specified in column 2 of the table in Part 2, 3 or 4 of Schedule 2 to Cap. 295E.
Where can you find the UN No. / PSN of the DG you possess?
As an international practice and required by paragraph 10 of Schedule 6 – Part 2 of the Dangerous Goods (Control) Regulation, the outer surface of an outermost packaging must be legibly marked with all of the following information:
- the UN No. of each type of S2DG contained in the packaging and, in the case of Class 3A DG, the HK number[4]; and
[4] Class 3A DG, which includes diesel, fuel oil and furnace oil, having a flash point exceeding 60oC (140oF) closed cup test, are not classified as DG in the UN System. Given there is no UN number for Class 3A DG, we have allocated a HK number – H301 to Class 3A DG.
- the proper shipping name or true name of each type of S2DG contained in the packaging, in either English or Chinese, as specified in the Code of Practice for Control of Dangerous Goods on Land[5].
[5] For further details, see 3.3.3 – “Marking Requirements” of the Code of Practice for Control of Dangerous Goods on Land.
True Name
“True name” can be a recognised chemical or other name currently used in scientific and technical handbooks, journals and texts or a name commonly used and understood by the trade and public having regard to the usage of the DG. Examples of “true name” are tabulated below:
|
Proper Shipping Name |
UN number |
True Name |
|
HYPOCHLORITE SOLUTION |
UN 1791 |
BLEACH |
|
PAINT RELATED MATERIAL |
UN 3066 |
THINNER |
Safety Data Sheet
Apart from checking the UN No. and proper shipping name from the outer surface of an outermost packaging, you may also request the DG manufacturer to provide you with a safety data sheet.
Safety data sheets provide information on chemical products, such as the hazards the chemical presents, and give information on handling, storage and emergency measures in case of accident. You may refer to Section 14 – “Transport Information” of your safety data sheet in which you can find the UN No., proper shipping name and other useful information, such as packing group of the DG you possess.
Are two substances having the same UN No. the same type of DG?
Type of DG[6]” is identified by the combination of the following information of the DG:
[6] Section 3 of Cap. 295E.
(a) UN No. / HK number;
(b) packing group (if any);
(c) proper shipping name;
(d) class; and
(e) subsidiary hazard (if any).
The following two DG bear the same UN No. albeit different:
- UN 1402 CALCIUM CARBIDE, PG I;
- UN 1402 CALCIUM CARBIDE, PG II
You may notice that the above two DG are assigned with different “PG” – packing group.
According to the degree of danger the chemical presents, either PG I, PG II or PG III will be assigned:
- Packing group I (PG I): Substances presenting high danger;
- Packing group II (PG II): Substances presenting medium danger; and
- Packing group III (PG III): Substances presenting low danger.
Packing group is a crucial information for you to understand the hazard of a DG and identify the DG correctly.