Regulation of Dangerous Goods
Main ContentChapter 2.3 Compatibility of DG
| 2.3.1 |
Legal Requirements |
|
|
|
| 2.3.1.1 |
Pursuant to section 110 of Cap. 295G:
(1) A person must not store, or cause or permit to be stored, 2 or more types of S2DG (whether or not of the same class) that are incompatible in a licensed store.
(2) For subsection (1), 2 or more types of S2DG are incompatible if, when they come into contact with each other or all others— (a) a combustion occurs or is likely to occur; (b) considerable heat is, or is likely to be, generated; (c) a flammable, asphyxiant, oxidizing or toxic gas is, or is likely to be, generated; (d) a corrosive substance is, or is likely to be, formed; or (e) a chemically unstable substance is, or is likely to be, formed.
(3) Without limiting subsection (1)— (a) Class 2 S2DG must not be stored with S2DG of a different class; (b) Class 3 S2DG must not be stored with S2DG of a different class, except Class 3A S2DG or paint materials that are Class 3 S2DG or Class 8 S2DG; (c) Class 3A S2DG must not be stored with S2DG of a different class, except Class 3 S2DG or paint materials that are Class 3 S2DG or Class 8 S2DG; and (d) Class 4 S2DG, Class 5 S2DG, Class 6.1 S2DG, Class 8 S2DG or Class 9 S2DG must not be stored with Class 2 S2DG, Class 3 S2DG or Class 3A S2DG, or S2DG of any other class so specified for the purposes of this paragraph in the code of practice.
(4) A person who contravenes subsection (1) commits an offence and is liable on conviction to a fine at level 4 and to imprisonment for 2 months. |
| 2.3.2 |
General Application |
|
|
|
| 2.3.2.1 |
Multiple types of DG shall not be stored together in a licensed store if they are incompatible. This chapter provides a practical guidance on how to determine the compatibility of DG to facilitate the application for a licensed store. To determine the compatibility of multiple types of DG, relevant compatibility tables at 2.3.3.2 and the compatibility groups and rules at column 10 of the DG List shall be observed. |
|
|
|
| 2.3.2.2 |
Considering the dangerous consequences and restrictions pursuant to section 110(2)&(3) of Cap. 295G as well as the packing requirements for the DG being complied with during storage of DG, the compatibility tables in 2.3.3.2 are prepared and compatibility groups and rules are assigned to DG at column 10 of the DG List for the purpose of determining the compatibility of different DG. |
|
|
|
| 2.3.2.3 |
The compatibility rules stated in this chapter do not apply to the storage of multiple types of DG when each type of DG does not exceed the GEQ / IEQ / SEQ (as the case may be) and the aggregate quantity does not exceed the aggregate EQ. |
| 2.3.3 |
Determining the Compatibility |
|
|
|
| 2.3.3.1 |
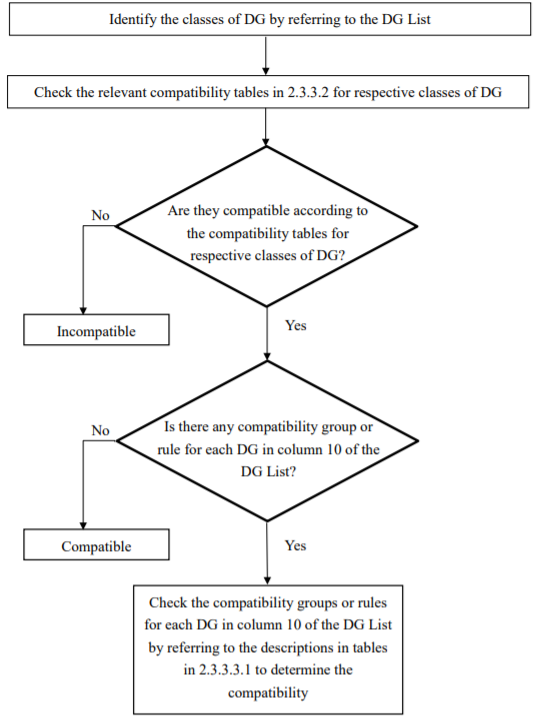
The methods on determining the compatibility of DG are as below and a flowchart is provided at 2.3.6 of this Chapter for easy reference:
(1) Identify the classes of DG by referring to the DG List; (2) Check the relevant compatibility tables in 2.3.3.2 for respective classes of DG. If it appears that the DG are incompatible, they are not allowed to be stored together in a licensed store. Otherwise, step (3) shall be followed; and (3) Check if there is any compatibility groups and compatibility rules for each DG at column 10 of the DG List: > if no, they are compatible; or > if yes, check the compatibility groups (CG) and compatibility rules (CR) for each DG at column 10 by making reference to the descriptions of CG and CR in tables in 2.3.3.3.1 to determine the compatibility. |
|
|
|
| 2.3.3.2 |
Compatibility Tables The general provisions for incompatibility between various classes of DG are shown in the “compatibility tables” below. In using the compatibility tables, the class of DG only denotes the primary hazard. Since the properties of different DG within each class may vary greatly, the column 10 of the DG List shall always be referred beforehand. Pursuant to section 110(3) of Cap. 295G, 3 compatibility tables are provided for the following 3 groups of DG classes respectively:
(1) Class 2.1, 2.2 & 2.3 DG (para. 2.3.3.2.1); (2) Class 3, 3A DG and paint materials that are Class 8 DG (para. 2.3.3.2.3); and (3) Class 4, 5, 6.1, 8 & 9 DG (para. 2.3.3.2.5). |
|
|
|
| 2.3.3.2.1 |
Compatibility Table for Class 2.1, 2.2 & 2.3 DG |
|
|
| CLASS | 2.1# | 2.2# | 2.3# | |
|
Flammable gases (2.1) |
O |
O |
X |
|
|
Non-flammable, non-toxic gases (2.2) |
O |
O |
O |
|
|
Toxic gases (2.3) |
X |
O |
O |
|
|
O Column 10 of the DG List shall be referred X Incompatible # Class 2 DG in limited packs are compatible with each other regardless of the table in 2.3.3.2.1 above and their CG & CR |
||||
|
|
|
| 2.3.3.2.2 |
Class 2 DG can be divided into 3 classes: (1) Class 2.1 DG – flammable gases; (2) Class 2.2 DG – non-flammable, non-toxic gases which include inert gases and oxidizing gases (compatibility groups shall be referred for oxidizing gases); and (3) Class 2.3 DG – toxic gases.
The compatibility of Class 2 DG are as follows:
(1) Class 2 DG is incompatible with any other classes of DG; (2) Flammable gases, oxidizing gases and toxic gases are incompatible with each other; (3) Inert gases are compatible with flammable gases, toxic gases and oxidizing gases (CG19 & CR7 shall be referred); and (4) Class 2 DG in limited packs are compatible with each other regardless of (2) and (3) above and their CG & CR. |
|
|
|
| 2.3.3.2.3 |
Compatibility Table for Class 3, 3A DG and paint materials that are Class 8 DG |
|
|
|
CLASS |
3# | 3A# | 8*# | |
|
Flammable liquids (3) |
O |
O |
O |
|
|
Diesel oils, furnace oils and other fuel oils (3A) |
O |
O |
O |
|
|
Paint materials (8*) |
O |
O |
O |
|
|
O Column 10 of the DG List shall be referred and Class 3 or 3A DG, which are immiscible27 with water, are incompatible with any such DG, which are miscible with water. * Only for paint materials that are Class 8 DG. # Class 3, 3A DG in limited packs and paint materials in limited packs are compatible with each other regardless of their miscibility and any CG & CR.
27 Miscibility of Class 3 / 3A DG are determined by methods stated in ASTM D1722-09 or relevant recognised national or international standards. |
||||
|
|
|
| 2.3.3.2.4 |
The compatibility of Class 3 or 3A DG are as follows: (1) Class 3 DG is incompatible with any other classes of DG except Class 3A DG or paint materials that are Class 3 or 8 DG; (2) Class 3A DG is incompatible with any other classes of DG except Class 3 DG or paint materials that are Class 3 or 8 DG; (3) Class 3 or 3A DG, which are immiscible with water, are incompatible with any such DG, which are miscible with water; and (4) Class 3, 3A DG in limited packs and paint materials ) in limited packs are compatible with each other regardless of their miscibility and any CG & CR. |
|
|
|
| 2.3.3.2.5 |
Compatibility Table of Class 4, 5, 6.1, 8 & 9 DG |
|
CLASS |
4.1# | 4.2# | 4.3# | 5.1# | 5.2# | 6.1# | 8# | 9# |
|
Flammable solids (4.1) |
O |
O |
O |
O |
X |
O |
O |
O |
|
Substances liable to |
O |
O |
O |
X |
X |
O |
O |
O |
|
Substances which, in contact with water, emit flammable gases (4.3) |
O |
O |
O |
X |
X |
O |
O |
O |
|
Oxidizing substances (5.1) |
O |
X |
X |
O |
X* |
O |
X |
O |
|
Organic peroxides (5.2) |
X |
X |
X |
X* |
O |
O |
X |
O |
|
Toxic substances (6.1) |
O |
O |
O |
O |
O |
O |
O |
O |
|
Corrosive substances (8) |
O |
O |
O |
X |
X |
O |
O |
O |
|
Miscellaneous dangerous substances or materials (9) |
O |
O |
O |
O |
O |
O |
O |
O |
|
O Column 10 of the DG List shall be referred X Incompatible * Class 5.1 or 5.2 DG in table 2.3.3.2.6 below are compatible with each other. # Regardless of the table in 2.3.3.2.5 above and CG & CR of the DG: (a) Class 4, 5, 6.1, 8 & 9 DG in limited packs are compatible with each other; and (b) Class 4, 5, 6.1, 8 & 9 DG which comprise the same substance but vary only in their water content are compatible with each other. |
|
Table 2.3.3.2.6 |
||||
| UN | Proper shipping name |
CLASS |
Subsidiary hazard(s) | Packing Group |
|
2014 |
HYDROGEN PEROXIDE, AQUEOUS SOLUTION |
5.1 |
8 |
II |
|
2984 |
HYDROGEN PEROXIDE, AQUEOUS SOLUTION |
5.1 |
- |
III |
|
3105 |
ORGANIC PEROXIDE TYPE D, LIQUID |
5.2 |
8 |
- |
|
3107 |
ORGANIC PEROXIDE TYPE E, LIQUID |
5.2 |
8 |
- |
|
3109 |
ORGANIC PEROXIDE TYPE F, LIQUID |
5.2 |
8 |
- |
|
3149 |
HYDROGEN PEROXIDE AND PEROXYACETIC ACID, MIXTURE, STABILIZED |
5.1 |
8 |
II |
| 2.3.3.3 |
Compatibility Group (CG) and Compatibility Rule (CR) |
|
|
|
| 2.3.3.3.1 |
For the purpose of determining compatibility, some DG are assigned with CG describing their chemical properties and CR describing their rules of compatibility. CG and CR are not applicable to DG in limited packs. The descriptions of various CG and CR are listed below and the CG and CR of different DG are provided in column 10 of the DG List. In utilizing the CG and CR, the class of DG only denotes the primary hazard regardless of their subsidiary hazards. |
|
Table - List of Compatibility Groups |
|
| Compatibility Group | Description |
|
CG1 |
Acids |
|
CG1a |
Strong acids |
|
CG2 |
Ammonium compounds |
|
CG3 |
Bromates |
|
CG4 |
Chlorates |
|
CG5 |
Chlorites |
|
CG6 |
Cyanides |
|
CG7 |
Heavy metals and their salts (including their organometallic compounds) |
|
CG8 |
Hypochlorites |
|
CG9 |
Lead and its compounds |
|
CG10 |
Liquid halogenated hydrocarbons |
|
CG11 |
Mercury and mercury compounds |
|
CG12 |
Nitrites and their mixtures |
|
CG13 |
Perchlorates |
|
CG14 |
Permanganates |
|
CG15 |
Powdered metals |
|
CG16 |
Peroxides |
|
CG17 |
Azides |
|
CG18 |
Alkalis |
|
CG19 |
Oxidizing gases (non-flammable & non-toxic) |
|
Table - List of Compatibility Rules |
|
| Compatibility Rule | Description |
|
CR1 |
For arsenic sulphides, incompatible with CG1 – acids or CG1a – strong acids |
|
CR2 |
Incompatible with CG1a – strong acids |
|
CR3 |
Incompatible with Class 5.1 DG |
|
CR4 |
Incompatible with Class 4.1 DG |
|
CR5 |
Incompatible with CG1 – acids or CG1a – strong acids |
|
CR6 |
Incompatible with CG18 – alkalis |
|
CR7 |
Incompatible with CG19 – oxidizing gases |
|
CR8 |
Incompatible with CG15 – powdered metals |
|
CR9 |
Incompatible with ammonia |
|
CR10 |
Incompatible with CG2 – ammonium compounds |
|
CR11 |
Incompatible with CG2 – ammonium compounds other than AMMONIUM PERSULPHATE (UN 1444) |
|
CR12 |
Incompatible with CG2 – ammonium compounds other than mixtures of ammonium persulphates and/or potassium persulphates and/or sodium persulphates |
|
CR13 |
Incompatible with CG3 – bromates |
|
CR14 |
Incompatible with bromine |
|
CR15 |
Incompatible with CG4 – chlorates |
|
CR16 |
Incompatible with chlorine |
|
CR17 |
Incompatible with CG5 – chlorites |
|
CR18 |
Incompatible with CARBON TETRACHLORIDE (UN 1846) |
|
CR19 |
Incompatible with CG6 – cyanides |
|
CR20 |
Incompatible with CG8 – hypochlorites |
|
CR21 |
Incompatible with iron oxide |
|
CR22 |
If flashpoint is 60°C or below, incompatible with Class 4.2, 4.3, 5.1 & 5.2 DG |
|
CR23 |
Incompatible with CG11 – mercury and mercury compounds |
|
CR24 |
Incompatible with mercury salts |
|
CR25 |
Incompatible with CG12 – nitrites |
|
CR26 |
Incompatible with CG13 – perchlorates |
|
CR27 |
Incompatible with CG14 – permanganates |
|
CR28 |
Incompatible with CG16 – peroxides |
|
CR29 |
Incompatible with sulphur |
|
CR30 |
Incompatible with Class 4.2, 4.3, 5.1 & 5.2 DG except DG of same class |
|
CR31 |
Incompatible with Class 4.2, 4.3, 5.2 & 8 DG except DG of same class |
|
2.3.3 |
Determining the Compatibility |
|
|
|
|
2.3.3.1 |
The methods on determining the compatibility of DG are as below and a flowchart is provided at 2.3.6 of this Chapter for easy reference:
(1) Identify the classes of DG by referring to the DG List; (2) Check the relevant compatibility tables in 2.3.3.2 for respective classes of DG. If it appears that the DG are incompatible, they are not allowed to be stored together in a licensed store. Otherwise, step (3) shall be followed; and (3) Check if there is any compatibility groups and compatibility rules for each DG at column 10 of the DG List: > if no, they are compatible; or > if yes, check the compatibility groups (CG) and compatibility rules (CR) for each DG at column 10 by making reference to the descriptions of CG and CR in tables in 2.3.3.3.1 to determine the compatibility. |
|
|
|
|
2.3.3.2 |
Compatibility Tables The general provisions for incompatibility between various classes of DG are shown in the “compatibility tables” below. In using the compatibility tables, the class of DG only denotes the primary hazard. Since the properties of different DG within each class may vary greatly, the column 10 of the DG List shall always be referred beforehand. Pursuant to section 110(3) of Cap. 295G, 3 compatibility tables are provided for the following 3 groups of DG classes respectively:
(1) Class 2.1, 2.2 & 2.3 DG (para. 2.3.3.2.1); (2) Class 3, 3A DG and paint materials that are Class 8 DG (para. 2.3.3.2.3); and (3) Class 4, 5, 6.1, 8 & 9 DG (para. 2.3.3.2.5). |
|
|
|
|
2.3.3.2.1 |
Compatibility Table for Class 2.1, 2.2 & 2.3 DG |
|
|
|
|
|
CLASS |
2.1# |
2.2# |
2.3# |
|
|
Flammable gases (2.1) |
O |
O |
X |
|
|
Non-flammable, non-toxic gases (2.2) |
O |
O |
O |
|
|
Toxic gases (2.3) |
X |
O |
O |
|
|
O Column 10 of the DG List shall be referred X Incompatible # Class 2 DG in limited packs are compatible with each other regardless of the table in 2.3.3.2.1 above and their CG & CR |
|||
|
|
|
|
2.3.3.2.2 |
Class 2 DG can be divided into 3 classes: (1) Class 2.1 DG – flammable gases; (2) Class 2.2 DG – non-flammable, non-toxic gases which include inert gases and oxidizing gases (compatibility groups shall be referred for oxidizing gases); and (3) Class 2.3 DG – toxic gases.
The compatibility of Class 2 DG are as follows:
(1) Class 2 DG is incompatible with any other classes of DG; (2) Flammable gases, oxidizing gases and toxic gases are incompatible with each other; (3) Inert gases are compatible with flammable gases, toxic gases and oxidizing gases (CG19 & CR7 shall be referred); and (4) Class 2 DG in limited packs are compatible with each other regardless of (2) and (3) above and their CG & CR. |
|
|
|
|
2.3.3.2.3 |
Compatibility Table for Class 3, 3A DG and paint materials that are Class 8 DG |
|
|
|
|
|
CLASS |
3# |
3A# |
8*# |
|
|
Flammable liquids (3) |
O |
O |
O |
|
|
Diesel oils, furnace oils and other fuel oils (3A) |
O |
O |
O |
|
|
Paint materials (8*) |
O |
O |
O |
|
|
O Column 10 of the DG List shall be referred and Class 3 or 3A DG, which are immiscible27 with water, are incompatible with any such DG, which are miscible with water. * Only for paint materials that are Class 8 DG. # Class 3, 3A DG in limited packs and paint materials in limited packs are compatible with each other regardless of their miscibility and any CG & CR.
27 Miscibility of Class 3 / 3A DG are determined by methods stated in ASTM D1722-09 or relevant recognised national or international standards. |
|||
|
|
|
|
2.3.3.2.4 |
The compatibility of Class 3 or 3A DG are as follows: (1) Class 3 DG is incompatible with any other classes of DG except Class 3A DG or paint materials that are Class 3 or 8 DG; (2) Class 3A DG is incompatible with any other classes of DG except Class 3 DG or paint materials that are Class 3 or 8 DG; (3) Class 3 or 3A DG, which are immiscible with water, are incompatible with any such DG, which are miscible with water; and (4) Class 3, 3A DG in limited packs and paint materials ) in limited packs are compatible with each other regardless of their miscibility and any CG & CR. |
|
|
|
|
2.3.3.2.5 |
Compatibility Table of Class 4, 5, 6.1, 8 & 9 DG |
|
CLASS |
4.1# |
4.2# |
4.3# |
5.1# |
5.2# |
6.1# |
8# |
9# |
|
Flammable solids (4.1) |
O |
O |
O |
O |
X |
O |
O |
O |
|
Substances liable to |
O |
O |
O |
X |
X |
O |
O |
O |
|
Substances which, in contact with water, emit flammable gases (4.3) |
O |
O |
O |
X |
X |
O |
O |
O |
|
Oxidizing substances (5.1) |
O |
X |
X |
O |
X* |
O |
X |
O |
|
Organic peroxides (5.2) |
X |
X |
X |
X* |
O |
O |
X |
O |
|
Toxic substances (6.1) |
O |
O |
O |
O |
O |
O |
O |
O |
|
Corrosive substances (8) |
O |
O |
O |
X |
X |
O |
O |
O |
|
Miscellaneous dangerous substances or materials (9) |
O |
O |
O |
O |
O |
O |
O |
O |
|
|
O Column 10 of the DG List shall be referred X Incompatible * Class 5.1 or 5.2 DG in table 2.3.3.2.6 below are compatible with each other. # Regardless of the table in 2.3.3.2.5 above and CG & CR of the DG: (a) Class 4, 5, 6.1, 8 & 9 DG in limited packs are compatible with each other; and (b) Class 4, 5, 6.1, 8 & 9 DG which comprise the same substance but vary only in their water content are compatible with each other. |
|
Table 2.3.3.2.6 |
||||
|
UN |
Proper shipping name |
CLASS |
Subsidiary hazard(s) |
Packing Group |
|
2014 |
HYDROGEN PEROXIDE, AQUEOUS SOLUTION |
5.1 |
8 |
II |
|
2984 |
HYDROGEN PEROXIDE, AQUEOUS SOLUTION |
5.1 |
- |
III |
|
3105 |
ORGANIC PEROXIDE TYPE D, LIQUID |
5.2 |
8 |
- |
|
3107 |
ORGANIC PEROXIDE TYPE E, LIQUID |
5.2 |
8 |
- |
|
3109 |
ORGANIC PEROXIDE TYPE F, LIQUID |
5.2 |
8 |
- |
|
3149 |
HYDROGEN PEROXIDE AND PEROXYACETIC ACID, MIXTURE, STABILIZED |
5.1 |
8 |
II |
|
2.3.3.3 |
Compatibility Group (CG) and Compatibility Rule (CR) |
|
|
|
|
2.3.3.3.1 |
For the purpose of determining compatibility, some DG are assigned with CG describing their chemical properties and CR describing their rules of compatibility. CG and CR are not applicable to DG in limited packs. The descriptions of various CG and CR are listed below and the CG and CR of different DG are provided in column 10 of the DG List. In utilizing the CG and CR, the class of DG only denotes the primary hazard regardless of their subsidiary hazards. |
|
Table - List of Compatibility Groups |
|
|
Compatibility Group |
Description |
|
CG1 |
Acids |
|
CG1a |
Strong acids |
|
CG2 |
Ammonium compounds |
|
CG3 |
Bromates |
|
CG4 |
Chlorates |
|
CG5 |
Chlorites |
|
CG6 |
Cyanides |
|
CG7 |
Heavy metals and their salts (including their organometallic compounds) |
|
CG8 |
Hypochlorites |
|
CG9 |
Lead and its compounds |
|
CG10 |
Liquid halogenated hydrocarbons |
|
CG11 |
Mercury and mercury compounds |
|
CG12 |
Nitrites and their mixtures |
|
CG13 |
Perchlorates |
|
CG14 |
Permanganates |
|
CG15 |
Powdered metals |
|
CG16 |
Peroxides |
|
CG17 |
Azides |
|
CG18 |
Alkalis |
|
CG19 |
Oxidizing gases (non-flammable & non-toxic) |
|
Table - List of Compatibility Rules |
|
|
Compatibility Rule |
Description |
|
CR1 |
For arsenic sulphides, incompatible with CG1 – acids |
|
CR3 |
Incompatible with Class 5.1 DG |
|
CR4 |
Incompatible with Class 4.1 DG |
|
CR5 |
Incompatible with CG1 – acids |
|
CR6 |
Incompatible with CG18 – alkalis |
|
CR7 |
Incompatible with CG19 – oxidizing gases |
|
CR8 |
Incompatible with CG15 – powdered metals |
|
CR9 |
Incompatible with ammonia |
|
CR10 |
Incompatible with CG2 – ammonium compounds |
|
CR11 |
Incompatible with CG2 – ammonium compounds other than AMMONIUM PERSULPHATE (UN 1444) |
|
CR12 |
Incompatible with CG2 – ammonium compounds other than mixtures of ammonium persulphates and/or potassium persulphates and/or sodium persulphates |
|
CR13 |
Incompatible with CG3 – bromates |
|
CR14 |
Incompatible with bromine |
|
CR15 |
Incompatible with CG4 – chlorates |
|
CR16 |
Incompatible with chlorine |
|
CR17 |
Incompatible with CG5 – chlorites |
|
CR18 |
Incompatible with CARBON TETRACHLORIDE (UN 1846) |
|
CR19 |
Incompatible with CG6 – cyanides |
|
CR20 |
Incompatible with CG8 – hypochlorites |
|
CR21 |
Incompatible with iron oxide |
|
CR22 |
If flashpoint is 60°C or below, incompatible with Class 4.2, 4.3, 5.1 & 5.2 DG |
|
CR23 |
Incompatible with CG11 – mercury and mercury compounds |
|
CR24 |
Incompatible with mercury salts |
|
CR25 |
Incompatible with CG12 – nitrites |
|
CR26 |
Incompatible with CG13 – perchlorates |
|
CR27 |
Incompatible with CG14 – permanganates |
|
CR28 |
Incompatible with CG16 – peroxides |
|
CR29 |
Incompatible with sulphur |
|
CR30 |
Incompatible with Class 4.2, 4.3, 5.1 & 5.2 DG except DG of same class |
|
CR31 |
Incompatible with Class 4.2, 4.3, 5.2 & 8 DG except DG of same class |
| 2.3.4 |
Final Scrutiny of the Application for Licensed Store |
|
|
|
| 2.3.4.1 |
The application for licensed store shall be subject to the final scrutiny by FSD with the assistance of the Government Laboratory. Test reports or documents issued by recognised laboratories verifying that the DG do not react dangerously with each other can be provided for further consideration. |
| 2.3.5 |
Examples of Determining Compatibility
The following examples illustrate how to determine compatibility of DG not in limited packs:
Example I Compatibility of PIPERAZINE (UN 2579) and ALUMINIUM CHLORIDE SOLUTION (UN 2581) |
|
|
| UN 2579 PIPERAZINE |
| Information | Meaning |
|
Class 8 |
Incompatible with Classes 2, 3 and 5.1 and 5.2 DG according to Compatibility Table |
|
CG18 |
Chemical property: alkalis |
|
CR5 |
Incompatible with CG1 – acids |
| UN 2581 ALUMINIUM CHLORIDE SOLUTION |
|
Information |
Meaning |
|
Class 8 |
Incompatible with Classes 2, 3 and 5.1 and 5.2 DG according to Compatibility Table |
|
CG1 |
Chemical property: acids |
|
CR6 CR19 |
Incompatible with CG18 – alkalis Incompatible with CG6 – cyanides |
|
(1) According to the DG List, UN 2579 and UN 2581 are Class 8 DG. (2) According to the compatibility table in 2.3.3.2.5, Class 8 DG are mutually compatible. Therefore, column 10 of the DG List shall be checked. (3) For UN 2579, column 10 of the DG List states “CG18” (Alkalis) and “CR5” (Incompatible with CG1 – acids). (4) For UN 2581, column 10 of the DG List states “CG1” (Acids), “CR6” (incompatible with CG18 – alkalis) and “CR19” (Incompatible with CG6 – cyanides). (5) According to CG18 of UN 2579 and CR6 of UN 2581, UN 2579 and UN 2581 are incompatible.
Example II Compatibility of SODIUM NITRATE (UN 1498) and MORPHOLINE (UN 2054) |
|
UN 1498 SODIUM NITRATE |
|
Information |
Meaning |
|
Class 5.1 |
Incompatible with Class 2, 3, 4.2, 4.3, 5.2 and 8 DG according to Compatibility Table |
|
UN 2054 MORPHOLINE |
|
Information |
Meaning |
|
Class 8 |
Incompatible with Classes 2, 3 and 5.1 and 5.2 DG according to Compatibility Table |
|
(1) According to the DG List, UN 1498 is Class 5.1 DG and UN 2054 is Class 8 DG. (2) According to the compatibility table in 2.3.3.2.5, Class 5.1 DG is incompatible with Class 8 DG. (3) Therefore, UN 1498 and UN 2054 are incompatible. |
| 2.3.6 |
Flowchart for Determining the Compatibility of DG
|
|
|